Home
/
Children's health
/
Yolk definition and methods of treatment and prevention of infection | health care
Yolk definition and methods of treatment and prevention of infection | health care
Yolk definition and methods of
treatment and prevention of infection
Definition of yolk
| --- | It occurs due to incomplete growth and maturation of the liver, and therefore cannot excrete the yellow matter.
| --- | unsatisfactory jaundice in babies often disappears within two weeks without any treatment just needing follow-up.
| --- | When treatment is neglected in advanced cases, the child may develop brain problems.
| --- | One of the most important ways to prevent breastfeeding (8 to 12 times a day) in the first days of life.
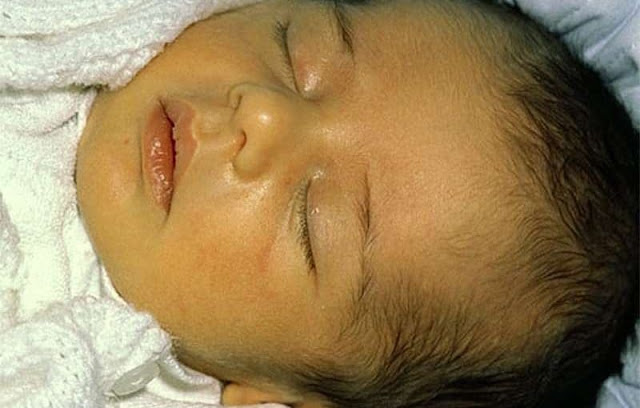
| --- | It is a common condition, especially in children born 38 weeks ago (preterm), and is caused by a rise in the yellow matter (bilirubin) in the blood, a substance that appears when old red blood cells break down to be replaced by new red blood cells, so that the yellow matter filtered into the liver and emerged Through feces.
Other names and causes of baby yolk
Jaundice - yolk - neonatal or congenital jaundice - yellowing in newborns.
Among the most important reasons: -
Natural yellowing
While the baby is in the womb, the placenta gets rid of the yellow material from his body, and after birth, the role of the liver begins to do this task, and you will need some time to complete its growth and do so very efficiently, so it cannot get rid of the yellow material before its completion, and this results in a natural yellowing In most newborns between two to four days old; As the percentage of yellow matter in the body does not exceed 200 micromol/liter, and it usually goes away within two weeks.
Pathological yellowing
1- Early yellowing: It occurs within less than 24 hours of the birth of the child, and its causes:
• breakdown of blood cells (such as maternal and child blood group mismatch, bean anemia).
• Infection: before childbirth (such as cat disease, rubella, syphilis), after childbirth.
Kriegler-Nagar syndrome.
2- Yellowing for a long time: It lasts for more than two weeks, and more than 21 days in preterm infants, and its causes:
• Infection (such as urinary tract infection).
• hypothyroidism.
Gastrointestinal problems (such as bile duct problems, neonatal hepatitis).
Symptoms of yolk, when should see a doctor?
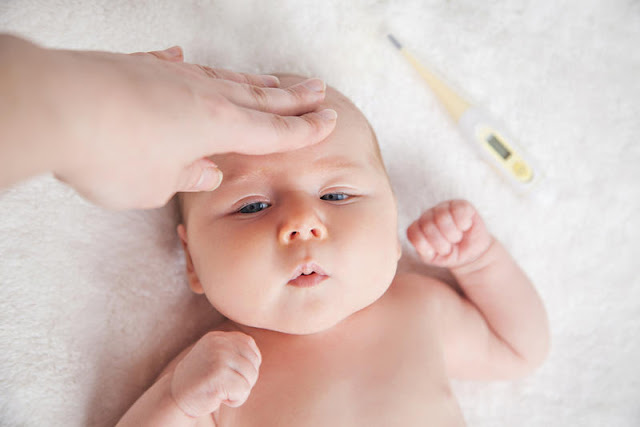
The baby will be examined within 72 hours of birth to check for jaundice, and you should see a doctor if there is an improvement in symptoms in the child after this time such as:
| --- | Increased skin yolk.
| --- | Difficulty awakening the child.
| --- | Not overweight.
| --- | High tone baby cry.
| --- | Reduced or rejected breastfeeding.
| --- | Jaundice persists for more than two weeks.
Diagnosis of the baby siren
| --- | Laboratory analysis: an examination of the yellow matter and additional tests if necessary.
Yolk risk factors
| --- | Family history of blood diseases.
| --- | Child malnutrition in the early days of his life.
| --- | Premature birth (premature infants).
| --- | Low birth weight.
| --- | Child bruising during childbirth.
| --- | The difference of blood type between mother and child.
| --- | Diabetic injury to the mother.
Complications of neonatal yolk
| --- | Deafness.
| --- | Cerebral palsy and other forms of brain damage.
Treatment and prevention
Often jaundice disappears in infants within two weeks without any treatment only needs follow-up, treatment is usually recommended only if tests show that the child has very high levels of yellow matter in the blood (more than 200 micromol/liter), and there are two main treatments Which can be performed in the hospital:
| --- | Light therapy that helps break down the yellow matter in the skin.| --- | In severe cases, the treatment is blood change.
| --- | Take care to breastfeed (8 to 12 times daily) in the first days of life.
| --- | Ensure the dates of the medical tests after birth.
| --- | Carefully monitor the baby the first five days after birth.















No comments