Home
/
Children's health
/
Childhood cancer its definition and causes treatment and prevention methods | health care
Childhood cancer its definition and causes treatment and prevention methods | health care
Childhood cancer its definition
and causes treatment and prevention methods
Definition of childhood cancer
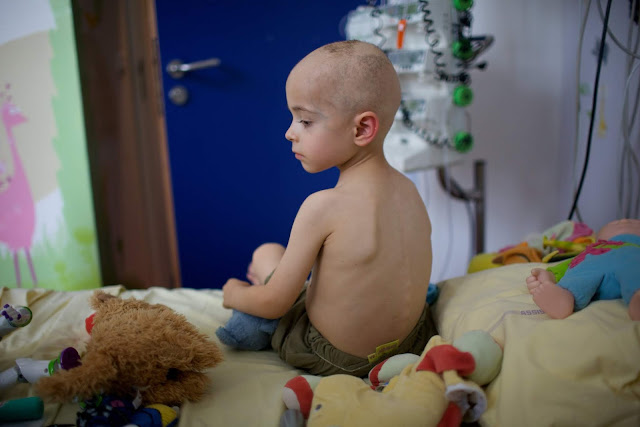
Cancer is a general term that includes a group of diseases that can affect all parts of the body. Cancer cells can divide quickly and abnormally, and can even grow beyond their known borders and storm into the contiguous parts of the body and spread to other organs. Twelve types of cancer may affect children. As leukemia and brain cancer are among the most common types of childhood cancer, the risk of developing cancer increases in infants while it decreases as they get older. The cause of childhood cancer is still unknown.
The causes of childhood cancer
The causes are unknown, but there are some conditions associated with Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities. Aging in parents may increase the risk of childhood cancer. Viral infections such as liver cancer (hepatitis B) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Exposure to ionizing radioactive materials in childhood may expose the child to cancer, especially leukemia.
Symptoms of childhood cancer
It depends on the type of cancer, the affected organ in the body, and the stage of the disease.
| --- | Leukemia may lead to anemia and frequent infections or may lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising.
| --- | Brain cancer causes frequent headaches and nausea when waking up in the morning, as well as general weakness and vision problems.
| --- | Cancer of the lymphatic system leads to swollen lymph nodes, high temperature and intense sweating in the evening.
Diagnosed with childhood cancer
| --- | Clinical examination of the patient.
| --- | Lab tests for leukemia and spinal cord fluid examination.
| --- | CT, TV and MRI scans.
| --- | Biopsy to take a tumor sample to determine the type.
Childhood cancer risk factors
Genetic factors are among the most important reasons.
Children who have been exposed to a large radiation dose are susceptible to infection, as well as those who have been exposed to chemicals or drugs and those with HIV, as there is a relationship between leukemia and HIV diseases, whether hereditary or acquired.
Childhood cancer complications
Cancer may lead to the emergence of several complications, including:
| --- | Cancer cells spread to the body.
| --- | Not responding to treatment or re-illness.
Treating childhood cancer
Childhood cancer treatment options:
| --- | Surgical treatment; To get rid of the tumor.
| --- | Chemotherapy; They are chemical drugs that kill cancer cells.
| --- | Radiation therapy with high-energy rays, such as X-rays.
| --- | Stem cells transplant by transferring the bone marrow, and it can be taken from the injured person's body or a donor.
Preventing childhood cancer
Avoid heavy exposure to the child.
| --- | Attention to feeding the child to raise his immunity.
| --- | If the child has a genetic disorder or genetic defect, he is required to follow up regularly with the geneticist.

















No comments